5.1.2 Model redshift
Condition: Because particles are striving to the 3 K-state wave-length that are smaller than lmax is made longer (shift to red of light). However, wave-lengths that are longer than lmax are made shorter (shift to blue of light).
Course of events: The shift results from the destruction of the l-structure that consists of three particles and the new formation of longer l (according the condition above).
The destruction and the new formation are caused by 3-particle- collisions. Certainly the destruction takes place on a sufficiently long way.
The shift (new wave-length) can be different. It is possible that there is a small shift with a part of DlDn=1 or a very large one that even can go to ¥ .
The most created wave-length is certainly the length lmax that is found most frequently.
With that is put in for Dllight: (lmax-l)
The new formation of a l has to take place in certain volume for the particle 2 and the particle 3. In the following these volumes are named "cube".
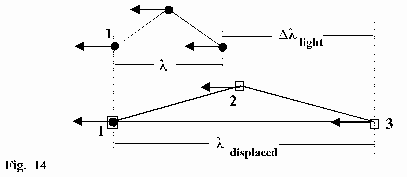
Drawing:

Wanted: The distance r at that l shifted itself by the value Dllight. Or in other words: the distance r is wanted until the particles 2 and 3 are in the above presented positions.
Conclusion: If particle 1 is in the cube above (in Fig.14 it is shown as a square), the particle 2 and the particle 3 must be generated by a 3-particle- collision. Furthermore they must have the correct direction.
The number of attempts for the generation of particle 2 is the same number of attempts as for one 3-particle-collision in the cube of particle 2:
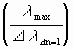
Moreover, by this generation the right direction must be found. For this condition as many attempts are needed as existing directions:
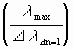 .
.
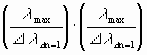
Exactly the same attempts are needed for particle 3. Consequently
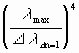 attempts are needed
in order to get a correct generation and direction for both particles 2 and 3.
attempts are needed
in order to get a correct generation and direction for both particles 2 and 3.
One attempt (3-particle-collision) takes place within a running-length
of lmax. The needed running-length for
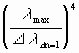 attempts is consequently:
attempts is consequently:
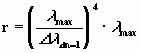
Thus Dllight, l and r is available for the left part of the equation.
Finally all values are put in the equation:
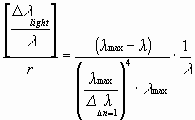
Here a dependence on the shift of l still exists.
If the values of lmax and DlDn=1 are put in following values of the shift will result for different l being within the visible light:
for
l=3*10-7 m:
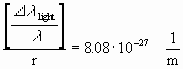 instead (5.41*10-27
1/m ±10%)
instead (5.41*10-27
1/m ±10%)
(short wavy bound of visible light)
for l=5.55*10-7
m:
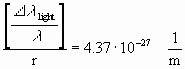
(maximum of intensity of sun about 5.5*10-7 m;
maximum of sensitiveness of human eye about 5.55*10-7 m)
for l=1*10-6
m:
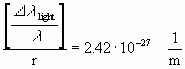
(long wavy bound of visible light)
Remark: The calculated shift is found in the known range but the dependence of the wave-length of light is unexpected. This fact is further to be investigated. (end of remark)